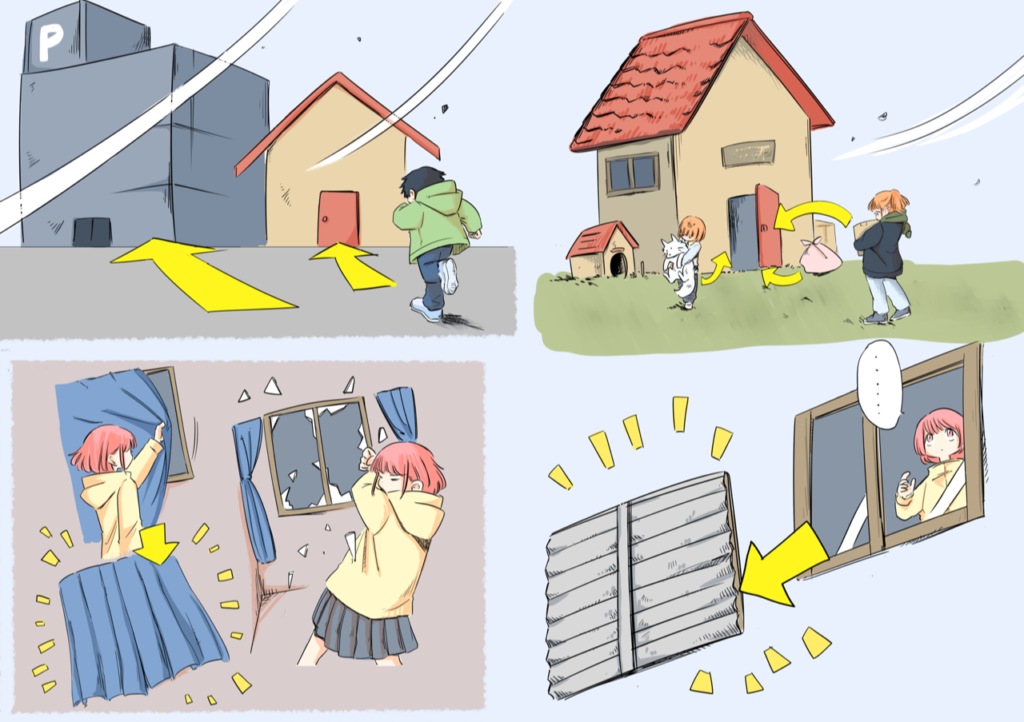
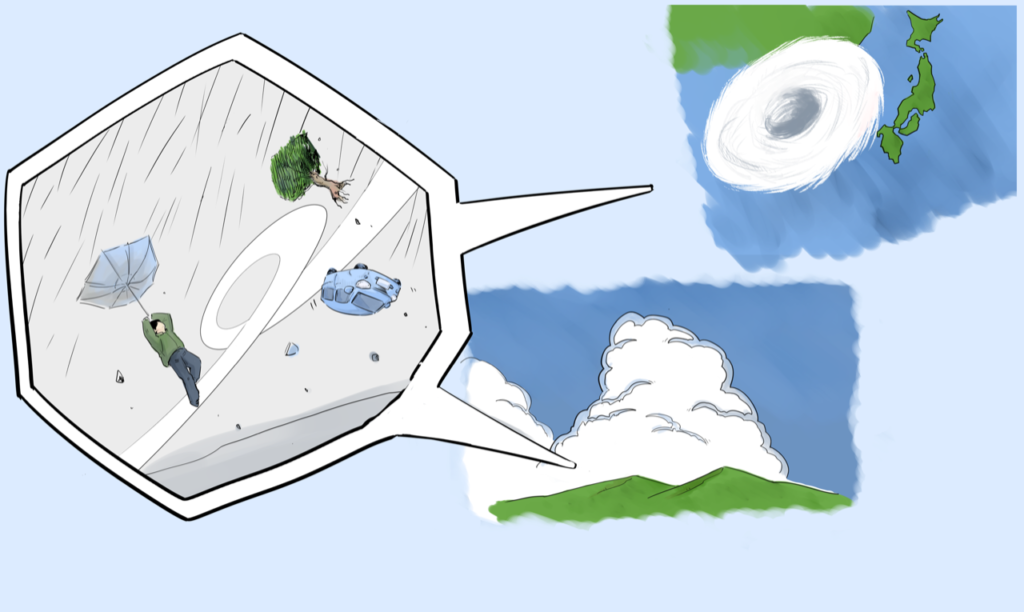
In the tropics, the sun’s intense rays heat the sea to over 27°C. The warm sea surface produces water vapor that rushes upward, which is the source of typhoons.
As the water vapor turns into droplets, it releases heat into the surrounding air, warming it and intensifying the updrafts that lead to the development of cumulonimbus clouds. At the bottom the air has risen, so the area below will cause the surrounding wind to blow in. This is called a tropical depression. When the wind speed exceeds 17.2 meters per second, it is called a “typhoon”.
It is called different names depending on the place where it occurs. For example, when it occurs in the North Atlantic Ocean or the Caribbean Sea, it is called a “hurricane”, while when it occurs in the Indian Ocean or around the Bay of Bengal, it is called a “cyclone”.