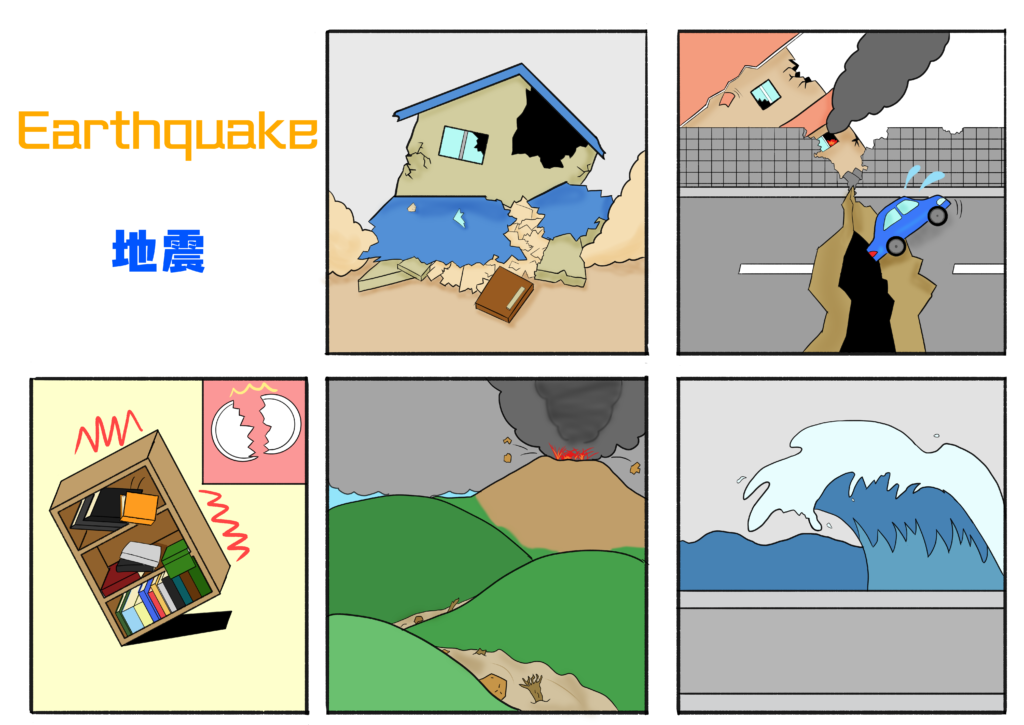
Pre-earthquake preparation
(1) Fix furniture firmly to the wall and do not place fragile or heavy objects on high places or at the head of the bed.
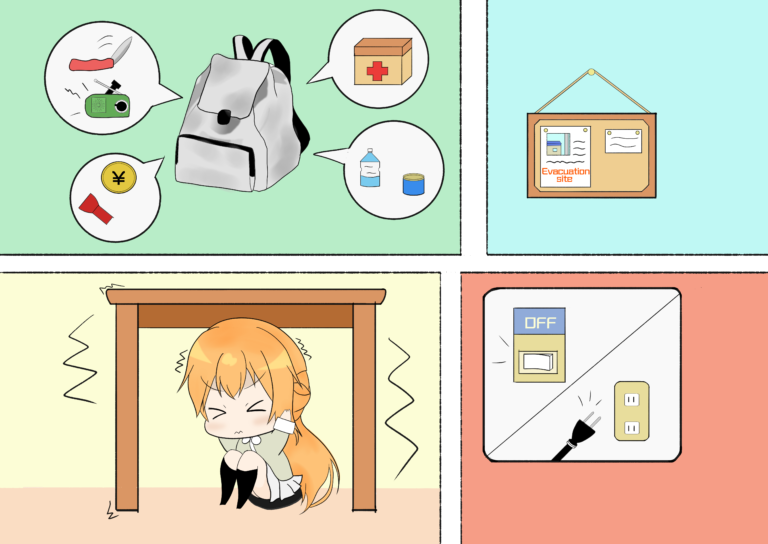
(2) Always have an emergency evacuation bag for disaster preparedness at home (containing emergency medical supplies, water, food, money, cold-weather clothes, towels, lights, portable knives, radio, contact cards, battery charger for cell-phone, etc.).
(3) Evacuation sites, parks, and contact information should be arranged with your family in advance.
In case of an earthquake
(1) First, lower your body posture and try to protect your head and neck with soft objects or hands.
(2) Shelter under a table or a solid barrier (doorway) and hold on.
After the earthquake stops shaking
(1) Check your home environment, quickly unplug electrical gadgets and switch off the power and gas.
(2) Take your emergency evacuation bag and open the door to escape from the building to an evacuation site.
(3) Contact your family to report the disaster and turn on your radio/cell-phone to listen to the latest disaster reports.
(4) If you are trapped, stay calm, try not exert too much energy, make some noise and wait for help.
(5) Also be prepared for aftershocks.