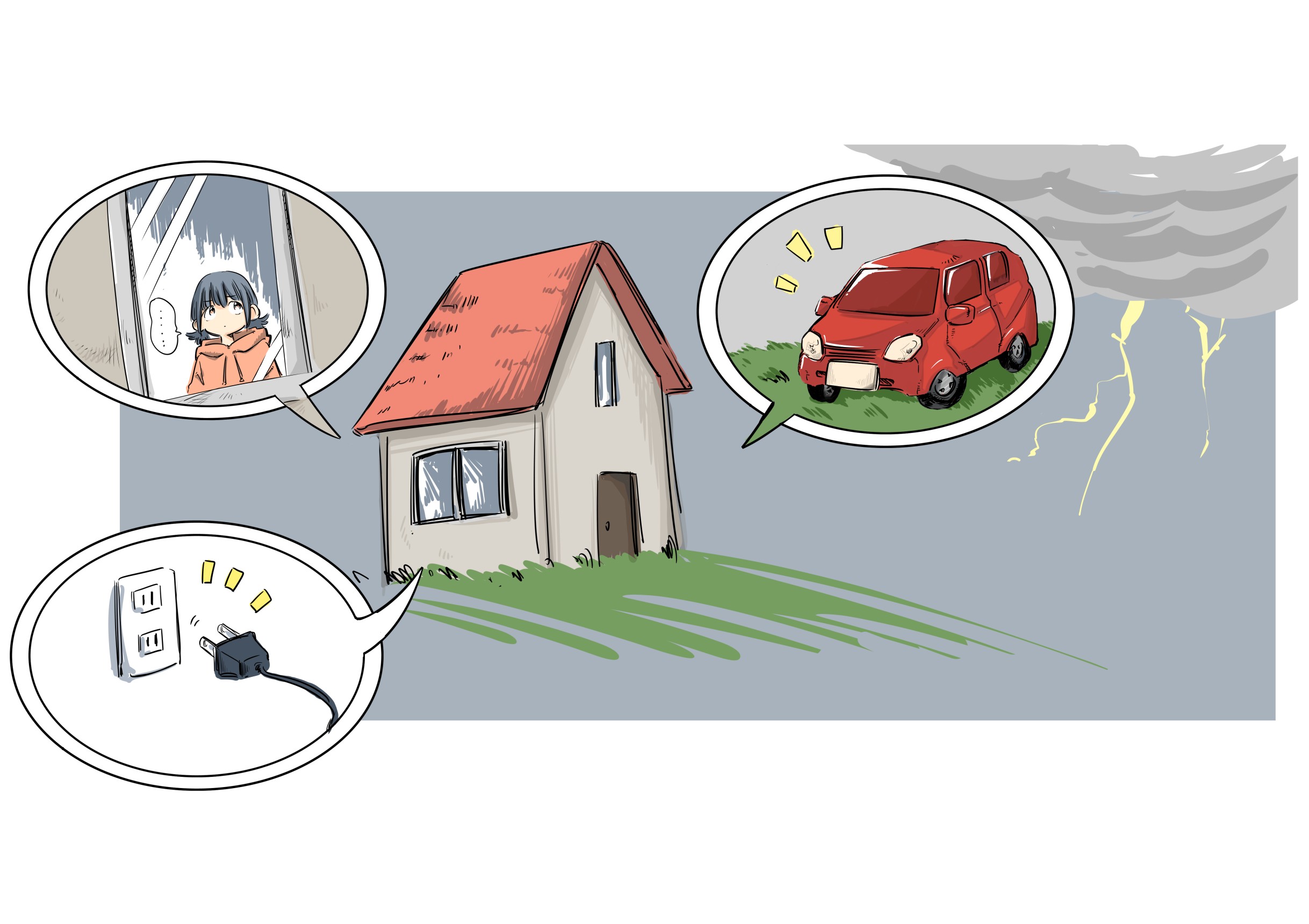
 1. If you hear thunder, seek shelter quickly in a nearreinforced concrete building or in a car. The best place to take shelter is in a reinforced concrete building, in the middle of a room or in a car.
1. If you hear thunder, seek shelter quickly in a nearreinforced concrete building or in a car. The best place to take shelter is in a reinforced concrete building, in the middle of a room or in a car.
2. Unplug appliances and turn off circuit breakers. Even indoors, proximity to poles and appliances can be dangerous. Lightning currents can also flow through wires and cables such as TV and telephone lines, so it is important to stay away from household appliances and avoid touching them. It is necessary to install protective equipment inside the building.
3. Do not take shelter from the rain on or under tall trees. When lightning strikes a tree, it will also pass through people close to the trunk. To avoid being struck lightning from a tree, keep at least two meters away from the tree branches.
4. Do not take shelter from the rain under the eaves. If lightning strikes the house where you are sheltering from the rain, a large current will flow through the eaves. It is more likely to pass through wetter bodies than through walls and columns that are less permeable to electricity, so the lightning current is likely to be carried partially on the side strike. The best place to take shelter from the rain is inside a building, not under the eaves.
5. If there is no place to take shelter nearby, keep as low a posture as possible.
6. Check the weather forecast and lightning forecast before leaving home.